The Input Shaft
Input shafts are made of heat-treated hardened steel. The shaft and the main drive gear are usually a one-piece assembly. The main gear is inside the case and always remains in constant mesh with the countershaft. The input shaft transfers torque from the clutch disk to the countershaft.
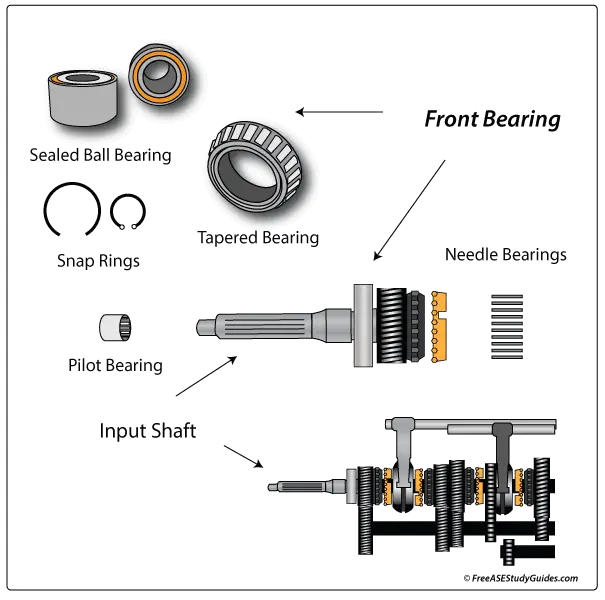
The transmission's front bearing or input shaft bearing's inner race is pressed onto the input shaft. The outer race is fastened to the transmission case by a retaining ring. It supports the inner portion of the shaft. A faulty front or input bearing is loudest when the clutch is fully engaged, and the input shaft is spinning at engine speeds.
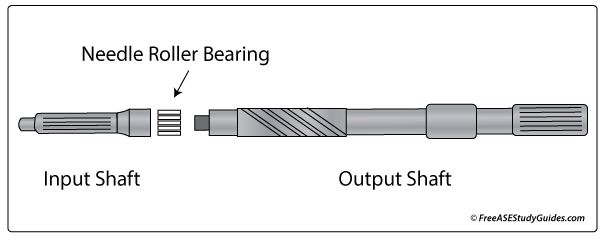
The input shaft connects to the output shaft with needle bearings. These bearings allow the input and output shaft to spin at different speeds. Faulty needle bearings make noise when the clutch is engaged, the vehicle is still, and the transmission is neutral. The input shaft spins at engine speed while the stationary vehicle holds the output shaft.
Shaft Endplay
Manual transmissions have an input, an output, and a countershaft. Manufacturers incorporate endplay into the input and output shafts for heat expansion and lubrication.
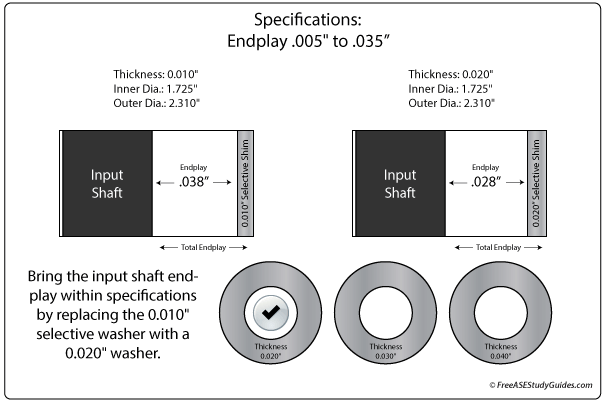
Measure the input and output shaft endplay before and after removal. Check end play with a dial indicator fastened to the case and the tip placed against the input shaft. If the reading is out of specification, look for worn or misassembled parts while disassembling the transmission. A thicker or thinner selective washer is typically installed to adjust the input shaft endplay.
Pilot Bearings
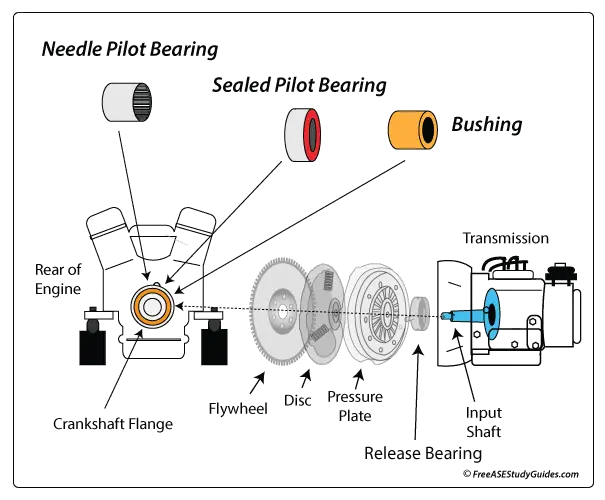
It's supported by bearings capable of rotating at high speeds. The pilot bearing supports the tip of the shaft and allows it to spin at a different speed than the engine's crankshaft. This difference in rotational speed occurs when the clutch is disengaged while the engine is running.
The pilot bearing is inside the engine's crankshaft flange. A faulty pilot bearing is loudest when the clutch pedal is completely depressed and the clutch is fully disengaged. The input shaft has slowed while the crankshaft still spins at engine speed. This difference in rotational speed works the pilot bearing, revealing its wear.