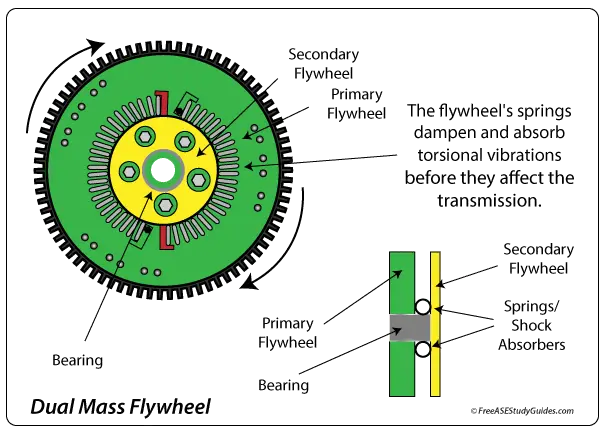
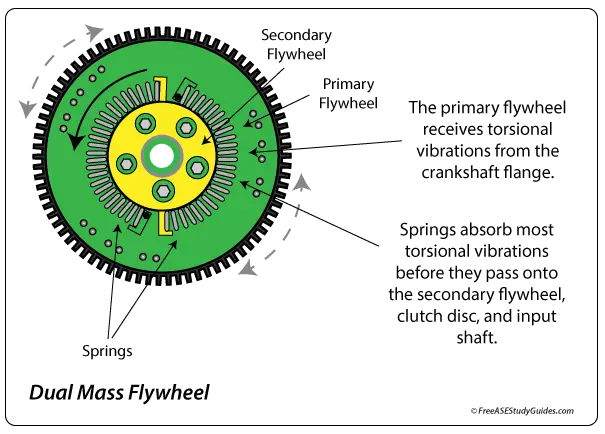
Dual Mass Flywheels
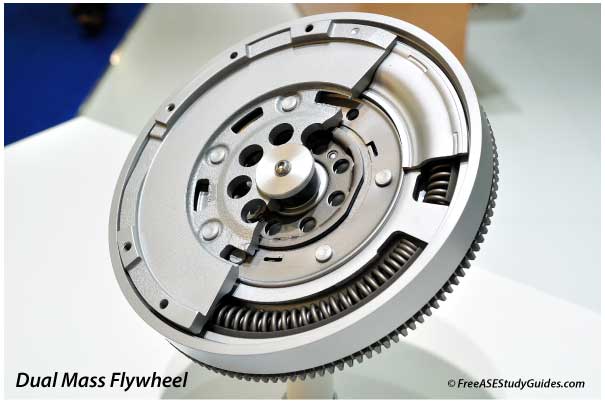

A dual-mass flywheel contains two plates, a bearing, and internal springs that absorb torsional vibrations. Today's diesel and powerful four-cylinder engines create a substantial power stroke. A dual-mass flywheel significantly reduces these engine pulses and driveline vibrations before they enter the drivetrain.
The internal springs weaken and break, causing excessive movement; this causes the secondary plate to oscillate, resulting in noise and driveline vibration. The severity depends on how bad the flywheel is; if it's just beginning to fail, there may be a rattling sound at cruise. The pitch changes as the clutch is engaged and disengaged. When completely worn, they make a loud rattling noise, usually noticeable at startup.
Dual Mass Flywheel Diagnosis
A new dual-mass flywheel has little movement between the plates; internal springs absorb the side-to-side movement. As the springs wear, this play increases. Read the manufacturer's specifications before proceeding. If the left-to-right play is over an inch, replace the flywheel. Most shops replace these flywheels with every clutch job.
Many vehicles have dual-mass flywheels, but they are expensive. They reduce torsional vibrations, primarily when the clutch first engages. Diesel engines and today's turbocharged four-cylinder engines benefit from these flywheels. The transmission must be separated from the engine to replace the flywheel.