(TFT) Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor
A (TFT) transmission fluid temperature sensor is one of several sensors providing input to the (TCM) transmission control module. It's located in the transmission or transaxle's valve body or oil pan. The TCM uses this sensor to monitor the temperature of the transmission fluid.
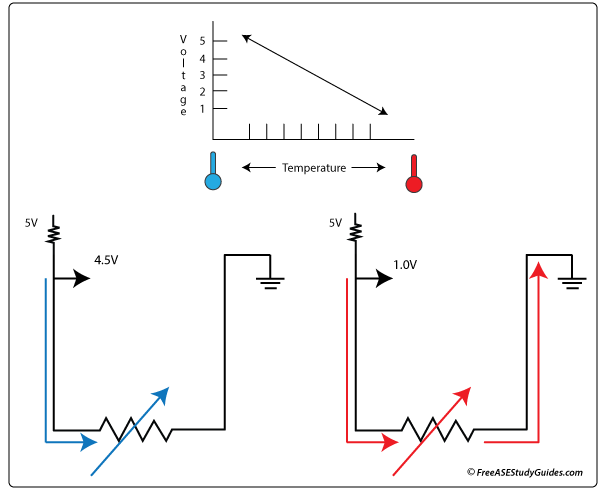
Thermistors change resistance as temperature changes. We know with Ohm's law that the voltage signal also changes as resistance changes. By increasing resistance, we lower the voltage signal sent to the TCM. Most transmission fluid temperature sensors are (NTC) or negative temperature coefficient sensors. The sensor's resistance decreases as the fluid's temperature increases.
The TFT and the TCC
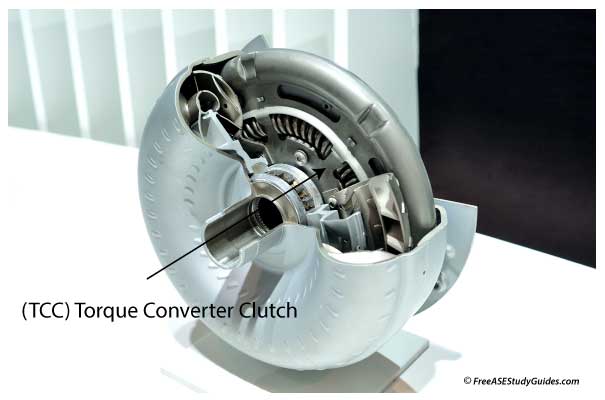
The TCM controls transmission operations using this input and other sensor inputs. When the fluid temperature is cold, the TCM delays (TCC) torque converter clutch engagement until the fluid reaches a specific temperature. The TCM engages the TCC mechanically, connecting the input shaft to the engine to cool the fluid if it gets too hot. If the fluid temperature reaches a threshold set by the manufacturer, 300° F or so, the TCM sets a fault code and illuminates the MIL to inform the driver. A faulty TFT sensor affects the torque converter and the transmission's line pressure.