Vacuum Brake Booster

Brake power assist units reduce pedal effort on automotive brake systems. When the booster fails to operate correctly, the brake pedal feels hard, and greater effort is needed to operate the brakes. This contrasts with a faulty master cylinder, typically resulting in a brake pedal that fades to the floor. Worn master cylinder cup seals cause this internal fluid leak.
Vacuum brake assist units require the proper amount of vacuum to operate correctly. This is an intake manifold vacuum (17-21 "hg), and an auxiliary pump can be used on some engines, particularly diesel. This vacuum is applied to both sides of the booster: the pedal side and the master cylinder side.
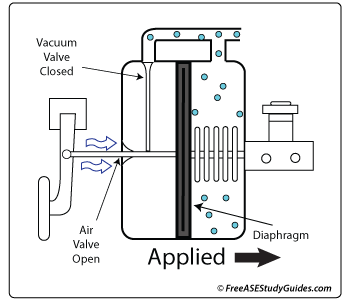
As the driver presses the brake pedal, the vacuum check valve blocks the vacuum source on the booster's peddle side. At the same time, it moves the air valve, allowing atmospheric pressure. Sometimes, a slight hissing noise can be heard as the air rushes past the filter, through the air valve, and into the chamber.
This collapse in vacuum on the pedal side, accompanied by the vacuum source still applied to the master cylinder side, produces a powerful brake assist. This is because of the flexible diaphragm located in the center of the assembly.
A rod or "power piston" is connected to this diaphragm. This push-rod is mechanically connected to the diaphragm and through the entire unit. One end is connected directly to the master cylinder and the other to the brake pedal. This is why vacuum brake booster failure does not result in a complete loss of braking action. There is always a mechanical connection between the two.
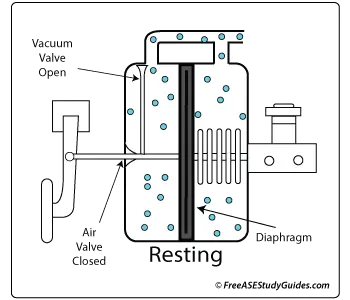
When the driver releases the brake pedal, a return spring located in the center of the master cylinder side of the booster assembly returns the diaphragm to its resting position. While the spring moves the diaphragm, the air and vacuum valves return to their at-rest positions. This returns the vacuum to both sides of the diaphragm. It's known as its balanced or at-rest position. Brake booster failure results in a hard brake pedal, making stopping much more difficult. A poor or restricted vacuum source also causes a hard brake pedal, robbing the booster of its vital vacuum source. A faulty air check valve causes the same problem.