Brake Caliper Piston Seals
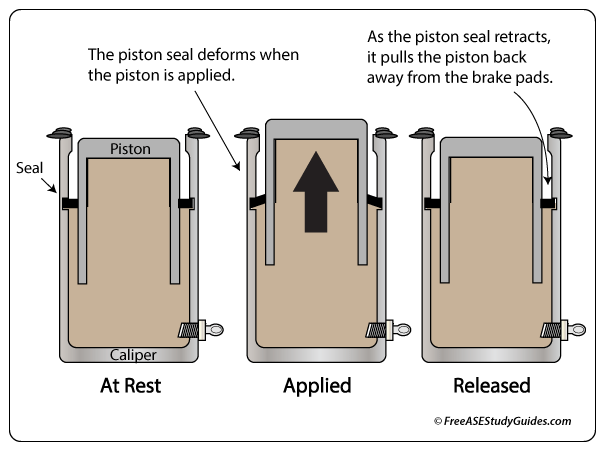
Except low drag brakes, disc brakes have little clearance between the brake pad and the rotor. As the piston seal retracts, it pulls the piston away from the rotor. If the pad does not retract properly, the brake can drag because the pad stays in contact with the rotor. This friction causes the rotor to overheat and deform. The vehicle drifts or pulls to the side that's dragging.
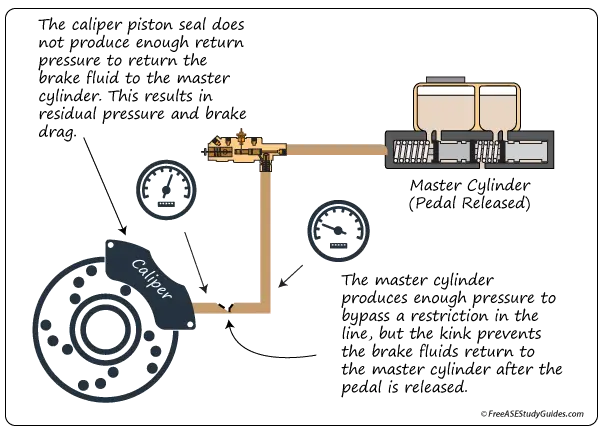
A restriction in the brake line also causes brake drag. The master cylinder creates enough pressure to bypass the kink, but the return pressure cannot bypass the restriction. The restriction leaves the brake applied.
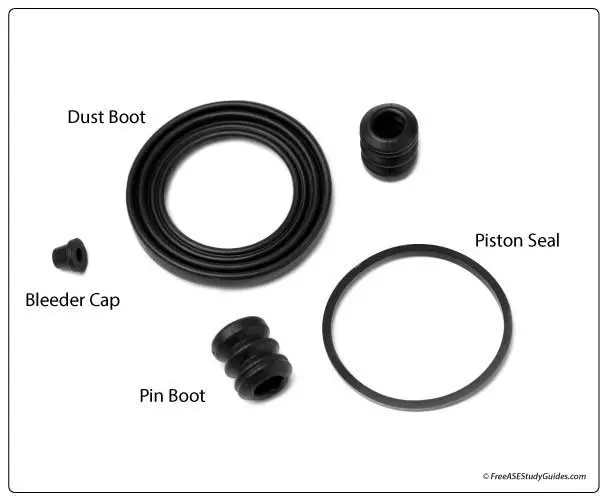

Brake calipers have a dust boot to protect the piston and seal from road debris and water. Inspect these boots for wear when replacing brake pads. Overhaul kits typically contain a new boot and seal. Square-cut piston seals and other rubber components are sensitive to water, oil, and contaminated brake fluid. Always lubricate the piston seal with clean brake or assembly fluid when rebuilding a brake caliper.