Brake Light Switch
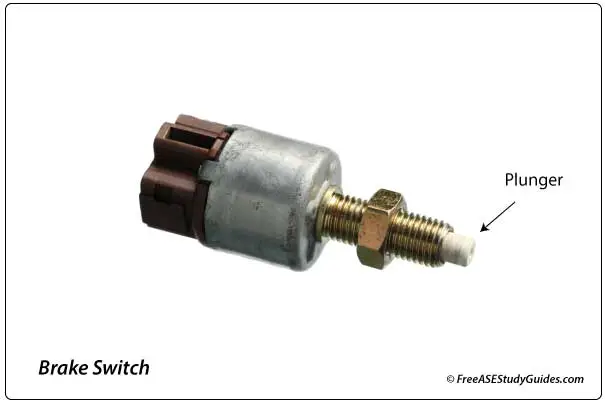
Most of today's vehicles have brake light switches mounted on the top of the brake pedal's arm. The brake lights, push-button ignition, shift interlock, cruise control, and ABS/TCS require this signal to function properly.
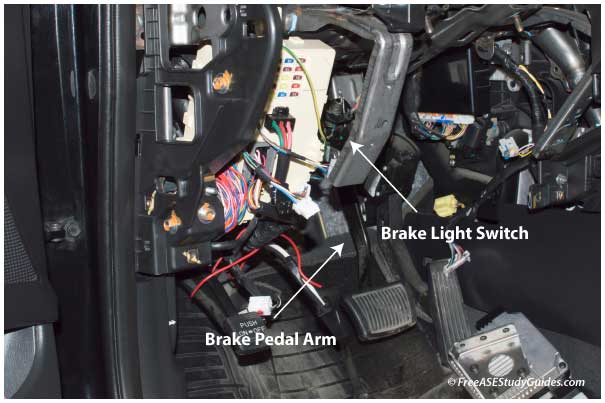
Use a scanner and a multimeter to diagnose and test the brake switch circuit. The connector on most brake switches contains four or more pins. Unfortunately, reaching a brake switch connector is often more challenging than testing it.
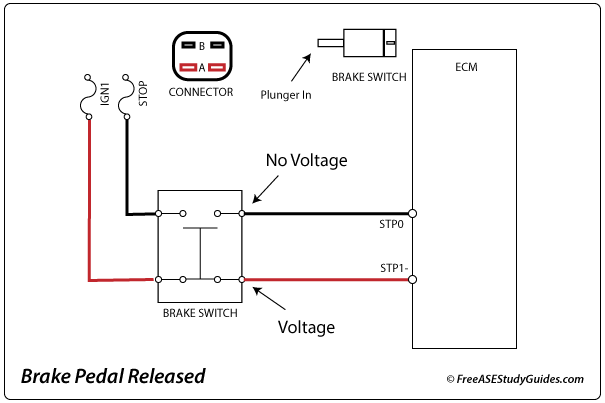
Brake switches typically signal a relay or control module. For example, with the pedal released, the brake switch illustrated above is (NO) open on one circuit and (NC) closed on the other. As a result, the control module receives a voltage signal on the (B STP1) pin but not on (A STP0).
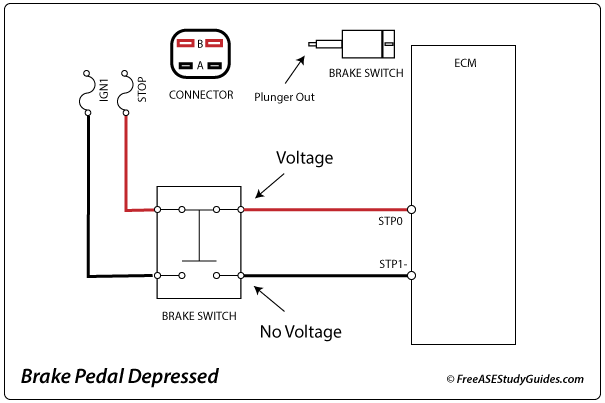
The control module responds when the pedal is depressed because the voltage signals switch. If these two signals are incorrect, the ECM will set a trouble code (P0504 BRAKE SWITCH A/B CORRELATION) and likely others. The following are common symptoms of a faulty brake switch.
No or Continuous Brake Light Operation

A blown brake light fuse or a faulty brake switch will result in no brake lights. Brake switches rarely fail, but the fuses and the small rubber brake switch pads/stoppers on the brake pedal do. The tab wears out, and the pad falls from the mounting onto the floorboard, resulting in continuous brake light operation. The steady current stresses the bulbs, the battery, and everything in between. A modern vehicle may not start or shift out of PARK when the switch or circuit fails.
Push Button Ignition

The driver must depress the brake pedal to start a vehicle with push button ignition. Therefore, the voltage signal from the brake switch is a must, and the engine will not start without it. In addition, the voltage signals from the brake switch must be correct for the ECM to shift an automatic transmission out of PARK or deactivate cruise control.
Shift Interlock

A vehicle with an automatic transmission will not shift out of PARK without the brake switch signal. A modern transmission requires the voltage signal from the brake switch to operate the shift interlock solenoid. A starting or shifter problem will result in fault codes, and a scan is in order. Most shifters have a release button for emergencies.
Cruise Control

A faulty brake switch will prevent the cruise control system from functioning. The ECM will disable cruise control and set code P0571 BRAKE SWITCH A CIRCUIT when there's a problem with the signal from the brake switch. The cruise control system uses the brake switch signal to deactivate the system when the brake pedal is depressed.
Stability Control Systems
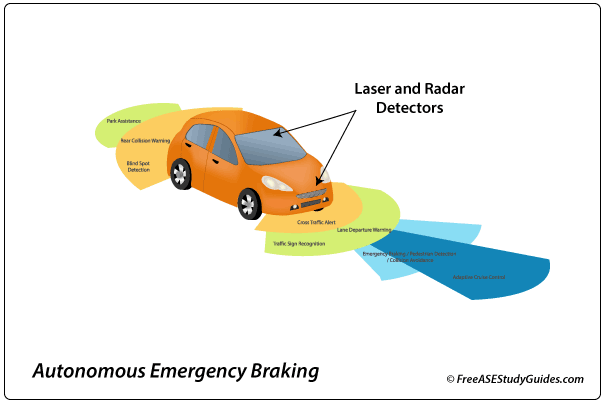
Modern vehicles with radar and AEB autonomous emergency braking systems can bypass the brake switch and activate the brakes in an emergency. Autonomous systems are computer-controlled and use lasers and radar for imaging, detecting, and ranging.
The ECM, EBCM, and BCM will illuminate warning lights on the instrument panel and set trouble codes if there's a problem with the switch or its circuit. Symptoms show up in pairs; if the transmission shifter does not shift out of PARK and the brake lights are out, the brake switch/circuit is likely at fault. Check the manual for TSBs and special testing procedures before troubleshooting the circuit.